China has considerably expanded its bailout lending as its Belt and Road Initiative blows up following a collection of debt write-offs, scandal-ridden tasks and allegations of corruption.
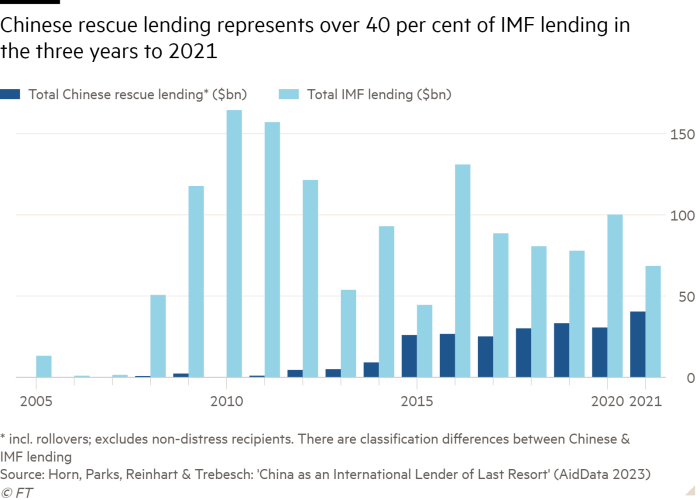
A research printed on Tuesday exhibits China granted $104bn price of rescue loans to creating nations between 2019 and the top of 2021. The determine for these years is nearly as massive because the nation’s bailout lending over the earlier 20 years.
The research by researchers at AidData, the World Financial institution, the Harvard Kennedy Faculty and the Kiel Institute for the World Economic system is the primary recognized try and seize complete Chinese language rescue lending on a world foundation.
Between 2000 and the top of 2021, China undertook 128 bailout operations in 22 debtor nations price a complete of $240bn.
China’s emergence as a extremely influential “lender of final resort” presents important challenges for the western-led establishments such because the IMF, which have sought to safeguard international monetary stability for the reason that finish of the second world struggle.
“The worldwide monetary structure is changing into much less coherent, much less institutionalised and fewer clear,” stated Brad Parks, govt director of AidData on the School of William and Mary within the US. “Beijing has created a brand new international system for cross-border rescue lending, but it surely has carried out so in an opaque and uncoordinated manner.”
Rising international rates of interest and the robust appreciation of the greenback have raised considerations concerning the capacity of creating nations to repay their collectors. A number of sovereigns have run into misery, with an absence of co-ordination amongst collectors blamed for prolonging some crises.
Sri Lanka president Ranil Wickremesinghe called on China and different collectors final week to shortly attain a compromise on debt restructuring after the IMF authorized a $3bn four-year lending programme for his nation.
China has declined to take part in multilateral debt decision programmes though it’s a member of the IMF. Ghana, Pakistan and different troubled debtors that owe massive quantities to China are intently watching Sri Lanka’s instance.
“[China’s] strictly bilateral method has made it harder to co-ordinate the actions of all main emergency lenders,” stated Parks.
A number of of the 22 nations that China has made rescue loans to — together with Argentina, Belarus, Ecuador, Egypt, Laos, Mongolia, Pakistan, Suriname, Sri Lanka, Turkey, Ukraine, and Venezuela — are additionally recipients of IMF help.
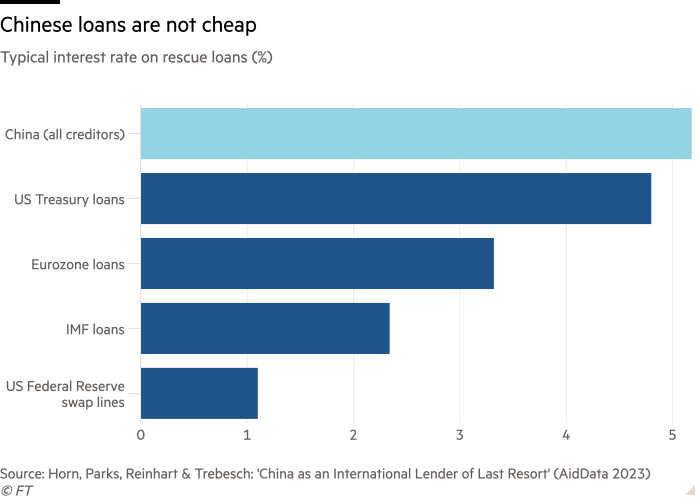
Nonetheless, there are massive variations between IMF programmes and Chinese language bailouts. One is that Chinese language cash shouldn’t be low cost. “A typical rescue mortgage from the IMF carries a 2 per cent rate of interest,” stated the research. “The typical rate of interest hooked up to a Chinese language rescue mortgage is 5 per cent.”
Beijing additionally doesn’t provide bailouts to all Belt and Highway debtors in misery. Huge recipients of Belt and Highway financing, which signify a major steadiness sheet threat for Chinese language banks, usually tend to obtain emergency support.
“Beijing is in the end attempting to rescue its personal banks. That’s why it has gotten into the dangerous enterprise of worldwide bailout lending,” stated Carmen Reinhart, a Harvard Kennedy Faculty professor and former chief economist on the World Financial institution Group.
China’s lending is in two types. The primary is thru a “swap line” facility, the place yuan is disbursed by the Folks’s Financial institution of China, the central financial institution, in return for home forex. Round $170bn was disbursed on this manner. The second is thru direct steadiness of funds help, with $70bn pledged, largely from state-owned Chinese language banks.
The Belt and Highway Initiative is the world’s largest-ever transnational infrastructure programme. The American Enterprise Institute, a Washington-based think-tank, has put the worth of China-led infrastructure tasks and different transactions categorised as “Belt and Highway” at $838bn between 2013 and the top of 2021.
The bailout bonanza reveals shortcomings within the design of a scheme described by Chinese language chief Xi Jinping as “the mission of the century”. One difficulty, stated Christoph Trebesch of the Kiel Institute, was that Chinese language lenders “actually went into many nations that turned out to have significantly extreme issues”.
Different deficiencies derived from a dearth of feasibility research and a common lack of transparency, in accordance with the research.
A number of tasks turned trigger célèbre for a way to not undertake growth lending. An notorious $1bn “street to nowhere” in Montenegro stays unfinished and dogged by corruption allegations, building delays and environmental points.
“White elephants” akin to Sri Lanka’s Hambantota port and Lotus Tower are seen as signs of the nation’s debt disaster, whereas greater than 7,000 cracks had been present in an Ecuadorean dam constructed by Chinese language contractors close to an lively volcano.








