[ad_1]
The world’s main central banks are poised to lift rates of interest this week to their highest ranges because the monetary disaster, stoking anxiousness amongst some traders that this month’s document bond market rally underestimates the rising proof of persistent inflation.
Bond costs have quickly rebounded because the begin of the 12 months from final 12 months’s historic sell-off, as markets guess that the tempo of coverage tightening will sluggish and, within the case of the US Federal Reserve, even back off. However some traders have doubts.
“I believe it’s only a matter of the market type of waking as much as what the macro atmosphere actually is, versus what they hope it’s,” stated Monica Erickson, head of funding grade credit score at DoubleLine Capital. “[It] goes to be tremendous troublesome once more for the Fed to . . . get inflation right down to that magical 2 per cent quantity with out placing us right into a recession.”
“The credit score markets are successfully pricing in a no-recession consequence. However that’s not the consensus base case that almost all economists are forecasting,” stated Maureen O’Connor, international head of high-grade debt syndicate at Wells Fargo.
A Bloomberg index monitoring high-grade and junk-rated authorities and corporate bonds around the globe has returned 3.3 per cent to this point in 2023, placing it on track for its strongest January since its inception in 1999. Inflows into US and western European company bond funds are set for his or her greatest January on document, totalling $19.3bn as much as January 26, in line with EPFR knowledge.
The Fed, the European Central Financial institution and the Financial institution of England will all maintain coverage conferences this week. Buyers count on the Fed to sluggish the tempo of its financial tightening to 0.25 proportion factors, elevating charges to the best degree since September 2007, the beginning of the worldwide monetary disaster.
The BoE and the ECB are broadly anticipated to carry charges by half a proportion level to their highest ranges since autumn 2008 when Lehman Brothers filed for chapter.
There are rising indications that underlying value pressures are proving persistent within the face of those fast and globally co-ordinated charge rises — and the hole between investor expectations and financial knowledge is widening.
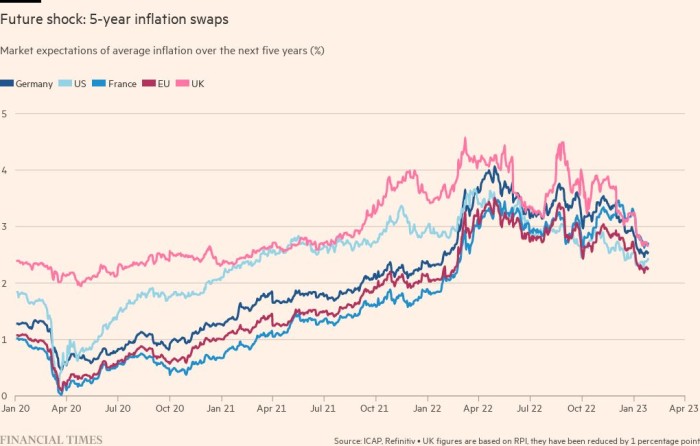
Market measures of inflation recommend merchants now count on inflation to ultimately fall near the Fed and ECB targets of two per cent. However value development nonetheless stands at 6.5 per cent within the US, and 9.2 per cent within the eurozone. Core inflation — which omits risky meals and vitality prices and is intently watched by central bankers — stays robust.
Shoppers and companies in most superior economies count on inflation to stay increased than central financial institution targets within the medium time period regardless of latest declines, surveys present. Policymakers intently watch such indicators, in addition to market-based measures of expectations, as a result of they’ll feed wage calls for, fuelling additional inflation.
“Inflation expectations generally is a self-fulfilling prophecy, as increased expectations set off the inflationary circumstances which might be envisioned,” stated Nathan Sheets, chief economist at US financial institution Citigroup. Central banks’ concern was “making certain that inflation expectations don’t ratchet upward from right here”.
Jennifer McKeown, chief international economist at Capital Economics, stated that “on nearly all measures, inflation expectations are nonetheless a lot increased than their pre-pandemic ranges and above the degrees that will be in step with the main banks’ 2 per cent inflation targets”.
If central banks maintain charges excessive for a protracted interval or elevate them by greater than traders count on, the bond market rally might unravel.
Yields on 10-year US Treasuries, a benchmark for borrowing prices throughout the globe, have slipped to three.5 per cent from 3.9 per cent on the finish of December. That has boosted the appeal of company bonds, which usually supply increased returns than their authorities counterparts.
Credit score spreads — the premium that traders demand to carry company bonds over high-grade authorities debt — have narrowed since the start of January. The hole in yields between US funding grade debt and Treasury notes has tightened by 0.1 proportion factors to this point this 12 months.
Spreads on lower-rated high-yield bonds have tightened even more, shedding nearly 0.6 proportion factors.
“The funding grade market is fairly priced for perfection proper now,” stated O’Connor. “I fear in regards to the black swan occasions and the catalysts that would catapult spreads wider from right here.”
Such considerations haven’t stopped a wave of money pouring into bond markets.
“There’s some huge cash chasing yields,” stated Rick Rieder, chief funding officer for mounted earnings at BlackRock. “In an atmosphere the place development is slowing, the place the fairness market will not be interesting, persons are saying — there’s a gorgeous yield and I can lock this charge up.”
[ad_2]
Source link