[ad_1]
sasha85ru | Getty Imates
In 2012, an industry-wide coalition of {hardware} and software program makers adopted Secure Boot to guard towards a long-looming safety risk. The risk was the specter of malware that would infect the BIOS, the firmware that loaded the working system every time a pc booted up. From there, it might stay resistant to detection and removing and will load even earlier than the OS and safety apps did.
The specter of such BIOS-dwelling malware was largely theoretical and fueled largely by the creation of ICLord Bioskit by a Chinese language researcher in 2007. ICLord was a rootkit, a category of malware that beneficial properties and maintains stealthy root entry by subverting key protections constructed into the working system. The proof of idea demonstrated that such BIOS rootkits weren’t solely possible; they have been additionally highly effective. In 2011, the risk turned a actuality with the invention of Mebromi, the first-known BIOS rootkit for use within the wild.
Keenly aware of Mebromi and its potential for a devastating new class of assault, the Safe Boot architects hashed out a posh new strategy to shore up safety within the pre-boot atmosphere. Constructed into UEFI—the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface that might turn into the successor to BIOS—Safe Boot used public-key cryptography to dam the loading of any code that wasn’t signed with a pre-approved digital signature. To today, key gamers in safety—amongst them Microsoft and the US National Security Agency—regard Safe Boot as an necessary, if not important, basis of belief in securing gadgets in a few of the most important environments, together with in industrial management and enterprise networks.
A vast Safe Boot bypass
On Thursday, researchers from safety agency Binarly revealed that Safe Boot is totally compromised on greater than 200 gadget fashions bought by Acer, Dell, Gigabyte, Intel, and Supermicro. The trigger: a cryptographic key underpinning Safe Boot on these fashions that was compromised in 2022. In a public GitHub repository dedicated in December of that yr, somebody working for a number of US-based gadget producers printed what’s often known as a platform key, the cryptographic key that varieties the root-of-trust anchor between the {hardware} gadget and the firmware that runs on it. The repository was situated at https://github.com/raywu-aaeon/Ryzen2000_4000.git, and it isn’t clear when it was taken down.
The repository included the non-public portion of the platform key in encrypted kind. The encrypted file, nevertheless, was protected by a four-character password, a choice that made it trivial for Binarly, and anybody else with even a passing curiosity, to crack the passcode and retrieve the corresponding plain textual content. The disclosure of the important thing went largely unnoticed till January 2023, when Binarly researchers discovered it whereas investigating a supply-chain incident. Now that the leak has come to mild, safety consultants say it successfully torpedoes the safety assurances supplied by Safe Boot.
“It’s a giant drawback,” mentioned Martin Smolár, a malware analyst specializing in rootkits who reviewed the Binarly analysis and spoke to me about it. “It’s principally a limiteless Safe Boot bypass for these gadgets that use this platform key. So till gadget producers or OEMs present firmware updates, anybody can principally… execute any malware or untrusted code throughout system boot. In fact, privileged entry is required, however that’s not an issue in lots of circumstances.”
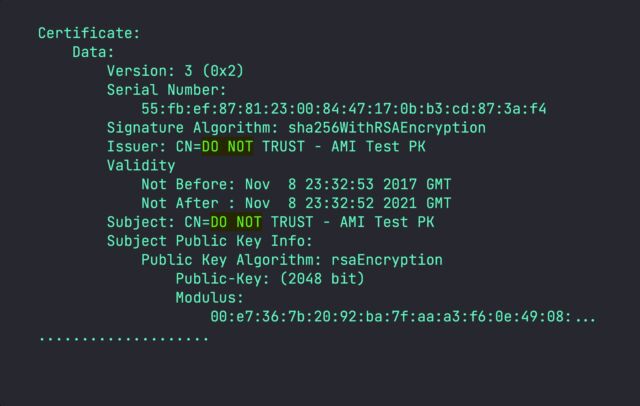
Binarly researchers mentioned their scans of firmware photographs uncovered 215 gadgets that use the compromised key, which could be recognized by the certificates serial quantity 55:fb:ef:87:81:23:00:84:47:17:0b:b3:cd:87:3a:f4. A desk showing on the finish of this text lists every one.
The researchers quickly found that the compromise of the important thing was just the start of a a lot larger supply-chain breakdown that raises critical doubts in regards to the integrity of Safe Boot on greater than 300 extra gadget fashions from just about all main gadget producers. As is the case with the platform key compromised within the 2022 GitHub leak, an extra 21 platform keys include the strings “DO NOT SHIP” or “DO NOT TRUST.”
Binarly
[ad_2]
Source link








