[ad_1]
Getty Photographs
Ransomware criminals have shortly weaponized an easy-to-exploit vulnerability within the PHP programming language that executes malicious code on net servers, safety researchers mentioned.
As of Thursday, Web scans carried out by safety agency Censys had detected 1,000 servers contaminated by a ransomware pressure generally known as TellYouThePass, down from 1,800 detected on Monday. The servers, primarily situated in China, not show their ordinary content material; as a substitute, many listing the positioning’s file listing, which reveals all information have been given a .locked extension, indicating they’ve been encrypted. An accompanying ransom observe calls for roughly $6,500 in change for the decryption key.
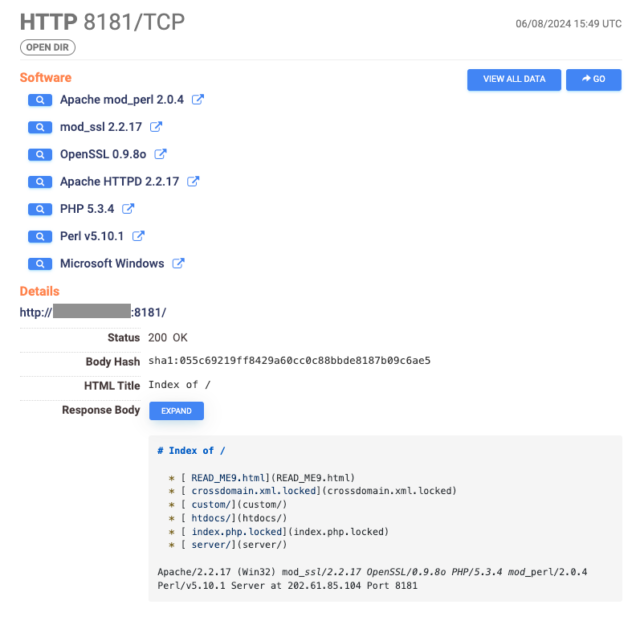
Censys

Censys
When alternative knocks
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-4577 and carrying a severity score of 9.8 out of 10, stems from errors in the way in which PHP converts Unicode characters into ASCII. A characteristic constructed into Home windows generally known as Greatest Match permits attackers to make use of a way generally known as argument injection to transform user-supplied enter into characters that cross malicious instructions to the principle PHP utility. Exploits permit attackers to bypass CVE-2012-1823, a crucial code execution vulnerability patched in PHP in 2012.
CVE-2024-4577 impacts PHP solely when it runs in a mode generally known as CGI, wherein an online server parses HTTP requests and passes them to a PHP script for processing. Even when PHP isn’t set to CGI mode, nonetheless, the vulnerability should still be exploitable when PHP executables resembling php.exe and php-cgi.exe are in directories which might be accessible by the net server. This configuration is extraordinarily uncommon, excluding the XAMPP platform, which makes use of it by default. A further requirement seems to be that the Home windows locale—used to personalize the OS to the native language of the consumer—have to be set to both Chinese language or Japanese.
The crucial vulnerability was printed on June 6, together with a security patch. Inside 24 hours, risk actors had been exploiting it to put in TellYouThePass, researchers from safety agency Imperva reported Monday. The exploits executed code that used the mshta.exe Home windows binary to run an HTML utility file hosted on an attacker-controlled server. Use of the binary indicated an strategy generally known as residing off the land, wherein attackers use native OS functionalities and instruments in an try and mix in with regular, non-malicious exercise.
In a post printed Friday, Censys researchers mentioned that the exploitation by the TellYouThePass gang began on June 7 and mirrored previous incidents that opportunistically mass scan the Web for weak methods following a high-profile vulnerability and indiscriminately focusing on any accessible server. The overwhelming majority of the contaminated servers have IP addresses geolocated to China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, or Japan, probably stemming from the truth that Chinese language and Japanese locales are the one ones confirmed to be weak, Censys researchers mentioned in an e-mail.
Since then, the variety of contaminated websites—detected by observing the public-facing HTTP response serving an open listing itemizing displaying the server’s filesystem, together with the distinctive file-naming conference of the ransom observe—has fluctuated from a low of 670 on June 8 to a excessive of 1,800 on Monday.
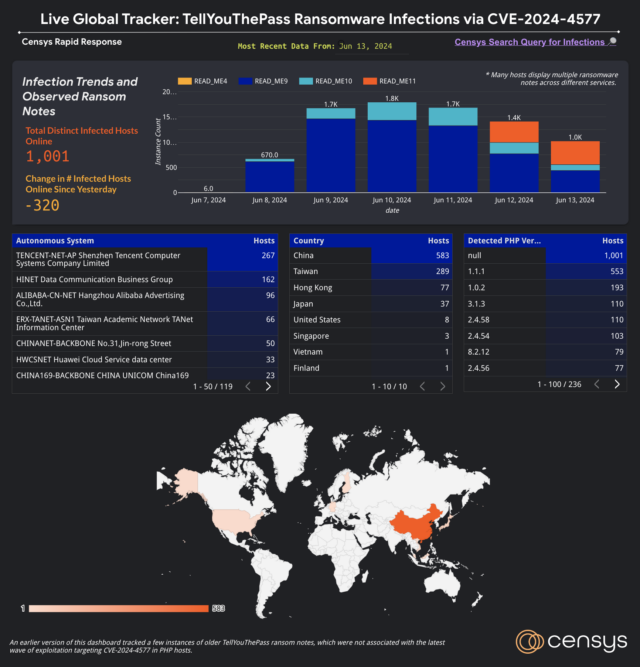
Censys
Censys researchers mentioned in an e-mail that they are not totally positive what’s inflicting the altering numbers.
“From our perspective, most of the compromised hosts seem to stay on-line, however the port working the PHP-CGI or XAMPP service stops responding—therefore the drop in detected infections,” they wrote. “One other level to contemplate is that there are presently no noticed ransom funds to the one Bitcoin tackle listed within the ransom notes (source). Based mostly on these info, our instinct is that that is probably the results of these providers being decommissioned or going offline in another method.”
XAMPP utilized in manufacturing, actually?
The researchers went on to say that roughly half of the compromises noticed present clear indicators of working XAMPP, however that estimate is probably going an undercount since not all providers explicitly present what software program they use.
“Provided that XAMPP is weak by default, it’s affordable to guess that a lot of the contaminated methods are working XAMPP,” the researchers mentioned. This Censys query lists the infections which might be explicitly affecting the platform. The researchers aren’t conscious of any particular platforms apart from XAMPP which were compromised.
The invention of compromised XAMPP servers took Will Dormann, a senior vulnerability analyst at safety agency Analygence, unexpectedly as a result of XAMPP maintainers explicitly say their software program isn’t appropriate for manufacturing methods.
“Folks selecting to run not-for-production software program need to take care of the results of that call,” he wrote in an internet interview.
Whereas XAMPP is the one platform confirmed to be weak, folks working PHP on any Home windows system ought to set up the replace as quickly as potential. The Imperva put up linked above gives IP addresses, file names, and file hashes that directors can use to find out whether or not they have been focused within the assaults.
[ad_2]
Source link








