[ad_1]
Getty Photographs
Malware just lately noticed within the wild makes use of subtle measures to disable antivirus protections, destroy proof of an infection, and completely infect machines with cryptocurrency-mining software program, researchers mentioned Tuesday.
Key to creating the unusually advanced system of malware function is a operate in the primary payload, named GhostEngine, that disables Microsoft Defender or every other antivirus or endpoint-protection software program that could be working on the focused laptop. It additionally hides any proof of compromise. “The primary goal of the GhostEngine malware is to incapacitate endpoint safety options and disable particular Home windows occasion logs, corresponding to Safety and System logs, which file course of creation and repair registration,” said researchers from Elastic Safety Labs, who found the assaults.
When it first executes, GhostEngine scans machines for any EDR, or endpoint safety and response, software program that could be working. If it finds any, it hundreds drivers recognized to comprise vulnerabilities that permit attackers to achieve entry to the kernel, the core of all working techniques that’s closely restricted to stop tampering. One of many susceptible drivers is an anti-rootkit file from Avast named aswArPots.sys. GhostEngine makes use of it to terminate the EDR safety agent. A malicious file named smartscreen.exe then makes use of a driver from IObit named iobitunlockers.sys to delete the safety agent binary.
“As soon as the susceptible drivers are loaded, detection alternatives lower considerably, and organizations should discover compromised endpoints that cease transmitting logs to their SIEM,” the researchers wrote, utilizing the abbreviation for safety info and occasion administration. Their analysis overlaps with recent findings from Antiy.
As soon as the EDR has been terminated, smartscreen.exe goes on to obtain and set up XMRig, a reliable utility for mining the monero cryptocurrency that’s typically abused by menace actors. A configuration file included causes all cash created to be deposited into an attacker-controlled pockets.
The an infection chain begins with the execution of a malicious binary that masquerades because the reliable Home windows file TiWorker.exe. That file runs a PowerShell script that retrieves an obfuscated script, titled get.png, which downloads extra instruments, modules, and configurations from an attacker-controlled server. Elastic Safety Labs supplied the next graphic that illustrates all the execution circulate:
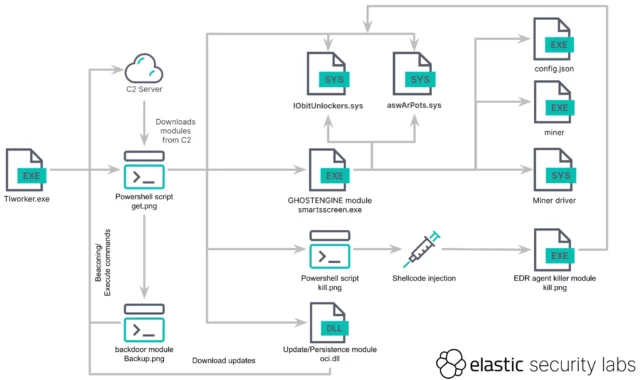
Elastic Safety Labs
GhostEngine additionally runs a number of recordsdata that permit the malware to achieve persistence, which means it hundreds every time the contaminated machine restarts. To do that, the file accountable, title get.png, creates the next scheduled duties with SYSTEM, the very best system privileges in Home windows:
- OneDriveCloudSync utilizing msdtc to run the malicious service DLL C:WindowsSystem32oci.dll each 20 minutes (described later)
- DefaultBrowserUpdate to run C:UsersPublicrun.bat, which downloads the get.png script and executes it each 60 minutes
- OneDriveCloudBackup to execute C:WindowsFontssmartsscreen.exe each 40 minutes.
A separate part can act as a backdoor that permits the attackers to additional obtain and execute malware on the contaminated machine. A PowerShell script titled backup.png “capabilities like a backdoor, enabling distant command execution on the system,” the researchers wrote. “It regularly sends a Base64-encoded JSON object containing a novel ID, derived from the present time and the pc title whereas awaiting base64-encoded instructions. The outcomes of these instructions are then despatched again.”
The researchers extracted the file the malware used to configure XMRig. It established a fee ID of:
468ED2Qcchk4shLbD8bhbC3qz2GFXqjAUWPY3VGbmSM2jfJw8JpSDDXP5xpkMAHG98FHLmgvSM6ZfUqa9gvArUWP59tEd3f
The ID allowed the researchers to view the employee and pool statistics on one of many Monero Mining Pool websites listed within the configuration.
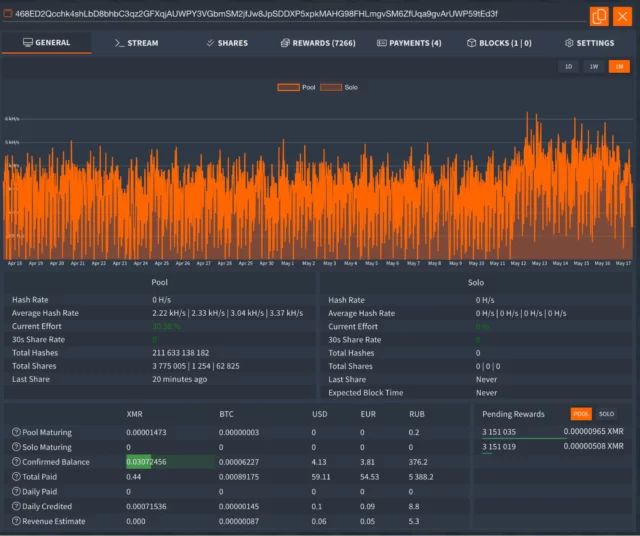
Elastic Safety Labs
The fee ID confirmed XMRig had netted the attackers solely a bit greater than $60. The researchers, nonetheless, famous that different machines contaminated in the identical marketing campaign can be given completely different IDs which will have generated bigger quantities of monero.
As a result of the marketing campaign efficiently disables an array of EDR protections, directors should depend on different means to find infections inside their networks. The researchers have launched a set of YARA guidelines that may flag infections. They work primarily by detecting the presence of the GhostEngine malware and the set up of the Avast and IOBit drivers. Tuesday’s put up additionally supplies an inventory of file hashes, IP addresses, and domains that may point out focusing on or an infection.
[ad_2]
Source link








