[ad_1]
ifanfoto/Getty Pictures
Two new research recommend that ransomware is not the profitable, enterprise-scale gotcha it was. Earnings to attackers’ wallets, and the proportion of victims paying, fell dramatically in 2022, in keeping with two separate reviews.
Chainalysis, a blockchain evaluation agency that has labored with numerous regulation enforcement and authorities businesses, suggests in a blog post that based mostly on funds to cryptocurrency addresses it has recognized as related to ransomware assaults, funds to attackers fell from $766 million in 2021 to $457 million final 12 months. The agency notes that its pockets knowledge doesn’t present a complete examine of ransomware; it needed to revise its 2021 complete upward from $602 for this report. However Chainalysis’ knowledge does recommend funds—if not assaults—are down since their pandemic peak.
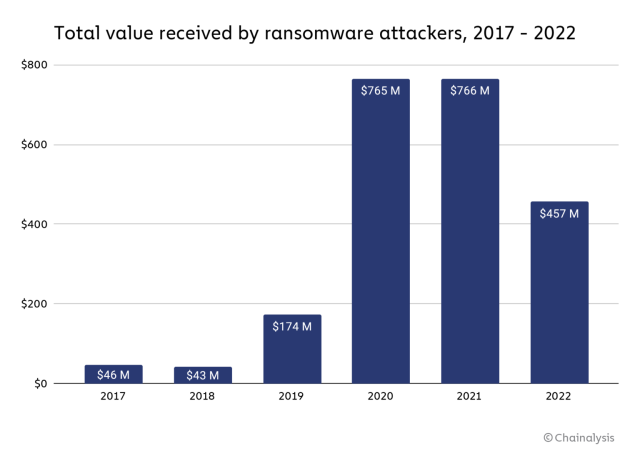
Chainalysis’ publish additionally exhibits attackers switching between malware strains extra shortly, and extra recognized attackers are holding their funds in mainstream cryptocurrency exchanges as an alternative of the illicit and funds-mixing locations that have been extra standard in ransomware growth instances. This may appear like an indication of a mature market with the next price of entry. However there’s extra to it than typical economics, Chainalysis suggests.
Smaller attackers typically swap between totally different ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) distributors performing numerous sorts of A/B exams on targets. And particular strains of malware convey totally different danger components to ransom negotiations. When Conti, a significant ransomware pressure, was discovered to be coordinating with the Kremlin and Russia’s Federal Safety Service (FSB), victims had another excuse—authorities sanctions—to not pay up. CD Projekt Purple, maker of the video games Cyberpunk 2077 and The Witcher, was one of the notable holdouts.
Conti’s leaders cut up up and ended up working inside numerous different ransomware teams, Chainalysis notes. So whereas ransomware could appear like an enormous market with 1000’s of individuals, it is nonetheless a small, traceable group of core actors that may be monitored.
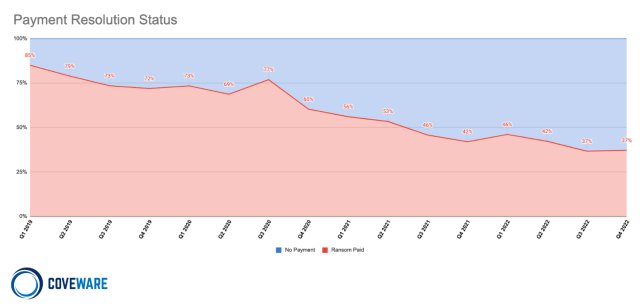
Cybersecurity evaluation agency Coveware is seeing similar trends, reporting that victims paying fell from 85 % in Q1 of 2019 to 37 % in This autumn 2022. The agency pins this on investments in safety and response planning, improvements in law enforcement recovering funds and arresting actors, and the compounding results of fewer funds pushing ransomware attackers out of the market.
-
Coveware’s knowledge suggests a marked spike within the common and median ransomware funds within the final quarter of 2022.
-
The median dimension of ransomware victims has been climbing steadily however has spiked within the final half of 2022, in keeping with Coveware’s knowledge.
Most of that strains up with Chainalysis’ report, however Coveware has a number of stunning statistics. The common and median ransom funds rose significantly within the final quarter of 2022 from simply the quarter earlier than. The median dimension of a ransomware sufferer additionally rose, with a specific spike to report ranges within the final half of 2022. Coveware suggests that is one other results of the non-payment squeeze on attackers. Concentrating on bigger companies permits for a bigger upfront demand, and extra companies try to re-extort victims—one thing beforehand practiced solely by smaller companies concentrating on smaller firms. “RaaS teams care lower than their predecessors about upholding their popularity,” Coveware’s publish explains. “Ransomware actors are initially pushed by economics, and when the economics are dire sufficient, they’ll stoop to ranges of deception and duplicity to recoup their losses.”
Extra knowledge, charts, and examples will be discovered on the weblog posts of Chainalysis and Coveware, as first spotted by Dark Reading.
[ad_2]
Source link








