[ad_1]
The eurozone will keep away from a recession this 12 months based on a widely-watched survey of economists which illustrates the sharp about-turn in international financial sentiment previously couple of weeks.
As not too long ago as final month, analysts surveyed by Consensus Economics have been predicting the bloc would plunge into recession this 12 months. However this month’s survey discovered that they now count on it to log progress of 0.1 per cent over the course of 2023. That is because of decrease power costs, bumper authorities assist and the earlier-than-anticipated reopening of the Chinese language financial system, which is about to spice up international demand.
The improve comes after officers and enterprise leaders at this week’s annual World Economic Forum in Davos additionally embraced a extra upbeat outlook, and the IMF signalled that it will quickly improve its forecasts for international progress.
Economists had feared that Europe can be among the many hardest-hit areas of the worldwide financial system this 12 months as a result of its publicity to the financial penalties of Russia’s struggle with Ukraine. Simply weeks in the past IMF managing director Kristalina Georgieva mentioned that “half of the European Union might be in a recession” throughout 2023.
Carsten Brzeski, head of macro analysis at ING Financial institution, described the about-turn in economists’ forecasts as “a recession that by no means got here”.
Susannah Streeter, analyst at Hargreaves Lansdown, mentioned: “The specter of the dreaded energy crisis [is] retreating, and inflation [is] climbing down extra quickly than anticipated.”
“Our perceptions have modified fairly radically since October,” mentioned Andrew Kenningham, chief Europe economist at Capital Economics, including authorities assist had been extra beneficiant than anticipated, whereas the auto sector has rebounded extra strongly than predicted.
There may be now lower than a 30 per cent likelihood of a recession, down from the an estimated 90 per cent final summer season, based on Anna Titareva, economist at UBS. She mentioned that the easing of provide chain disruptions, a robust labour market and extra financial savings clarify the eurozone’s financial resilience, and Europe has been profitable in filling its fuel storage in latest months, which has significantly diminished fears of fuel rationing.
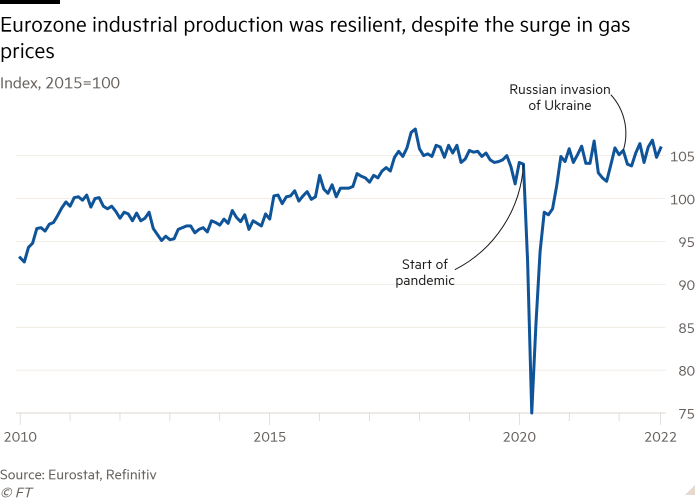
The latest sharp fall in wholesale gas prices again to ranges final seen earlier than Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has additionally helped increase the financial outlook. JPMorgan this week raised its 2023 eurozone GDP forecast to 0.5 per cent after anticipating pure fuel costs can be about €76 per megawatt hour, moderately than its earlier expectation of €155.
Talking at Davos this week Christine Lagarde, president of the European Central Financial institution, mentioned the financial prognosis was wanting “rather a lot higher” than feared. Gita Gopinath, the IMF’s deputy managing director, mentioned China’s choice final month to ease Covid-19 restrictions was one motive why the fund had develop into extra optimistic.
Sven Jari Stehn, economist at Goldman Sachs, mentioned firmer demand in China would “increase European commerce considerably, particularly in Germany”.
German chancellor Olaf Scholz mentioned this week he was “satisfied” Europe’s largest financial system wouldn’t fall right into a recession. Banque de France governor François Villeroy de Galhau mentioned: “For Europe, we must always keep away from a recession this 12 months, which I wouldn’t have mentioned with such confidence three months in the past.”
Some economists do nonetheless count on a recession. Silvia Ardagna, economist at Barclays Financial institution, mentioned that whereas the downturn wouldn’t be as deep as beforehand thought, the eurozone financial system would nonetheless contract for 2 successive quarters — assembly the technical definition of a recession.
Kenningham warned aggressive fee will increase by the ECB might result in a weak restoration.
Lagarde signalled in Davos the ECB would elevate charges by 50 foundation factors at its February and March conferences. The deposit fee has already elevated by 2.5 share factors to 2 per cent since June final 12 months, a tempo of tightening that eurozone economies haven’t skilled earlier than.
“The eurozone financial system might keep away from a recession however rates of interest might have to remain excessive for a protracted interval,” mentioned Kenningham. “It appears like we might get — at worst — a light recession, however that might be adopted by a weak restoration.”
[ad_2]
Source link








