[ad_1]
Getty Photos
Tutorial researchers have found severe vulnerabilities within the core of Threema, an immediate messenger that its Switzerland-based developer says supplies a degree of safety and privateness “no different chat service” can provide. Regardless of the unusually robust claims and two impartial safety audits Threema has acquired, the researchers mentioned the failings utterly undermine assurances of confidentiality and authentication which are the cornerstone of any program bought as offering end-to-end encryption, sometimes abbreviated as E2EE.
Threema has greater than 10 million customers, which embody the Swiss authorities, the Swiss military, German Chancellor Olaf Scholz, and different politicians in that nation. Threema builders promote it as a safer different to Meta’s WhatsApp messenger. It’s among the many prime Android apps for a fee-based class in Switzerland, Germany, Austria, Canada, and Australia. The app makes use of a custom-designed encryption protocol in contravention of established cryptographic norms.
The seven lethal flaws
Researchers from the Zurich-based ETH analysis college reported on Monday that they discovered seven vulnerabilities in Threema that significantly name into query the true degree of safety the app has supplied over time. Two of the vulnerabilities require no particular entry to a Threema server or app to cryptographically impersonate a consumer. Three vulnerabilities require an attacker to realize entry to a Threema server. The remaining two will be exploited when an attacker features entry to an unlocked cellphone, equivalent to at a border crossing.
Paterson et al.
“In totality, our assaults significantly undermine Threema’s safety claims,” the researchers wrote. “All of the assaults will be mitigated, however in some circumstances, a serious redesign is required.”
The seven vulnerabilities the researchers uncovered embody:
- Exterior actor with no particular entry
- Within the occasion an ephemeral key’s uncovered even as soon as, an attacker can completely impersonate the shopper to the server after which acquire all metadata in all E2EE messages. It is a outstanding shortcoming as a result of ephemeral keys ought to by no means have the ability to authenticate a consumer. With Threema, leaking of an ephemeral key has the identical impact as leaking a long-term key. Sloppy key administration additionally causes Threema to reuse ephemeral keys in locations they need to by no means be reused.
- A flaw in the way in which Threema’s client-to-server (C2S) protocol interacts with its end-to-end (E2E) protocol that causes a consumer to create a particular Threema worth often called a vouch field and ship it to the attacker. The attacker can exploit it by tricking a consumer into sending a set of characters (u9j6ߓ’jjखԻ^߃1כW:-́;ܡRA) to a particular however innocuous account. One attainable manner for an attacker to do that is to ship spam to numerous customers that tells them to ship the character string to a particular account so as to be eligible for a prize. From that time on, the attacker can impersonate the hacked shopper to the server.
 Enlarge / Assault 1.2 in observe: on the left, an acceptable keypair that’s base64 encoded. The general public key bytes 1 to 31 , additionally encoded within the QR code, all include printable UTF-8 characters. On the precise, the *LYTAAAS Threema gateway account (since revoked), with the hijacked public key of the server. Consumer U sending the contents of the QR to *LYTAAAS as a message will enable *LYTAAAS to authenticate to Threema because the U.
Enlarge / Assault 1.2 in observe: on the left, an acceptable keypair that’s base64 encoded. The general public key bytes 1 to 31 , additionally encoded within the QR code, all include printable UTF-8 characters. On the precise, the *LYTAAAS Threema gateway account (since revoked), with the hijacked public key of the server. Consumer U sending the contents of the QR to *LYTAAAS as a message will enable *LYTAAAS to authenticate to Threema because the U.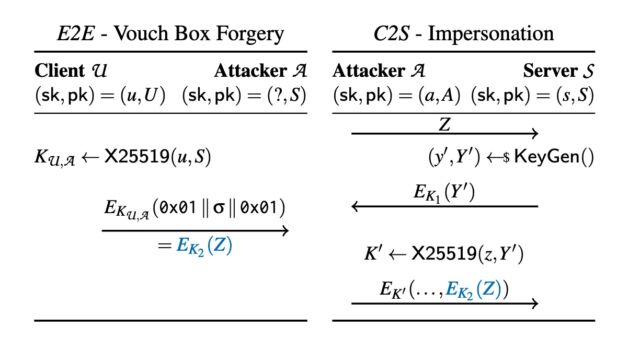 Enlarge / A determine exhibiting the cross-protocol interplay of an E2E and a C2S session. The attacker claims the general public key of the server and is aware of a keypair of the shape (z, Z = 0x01 ∥ σ ∥ 0x01). They persuade the sufferer U to ship σ to them as an E2E textual content message (in blue, Left aspect). The attacker can now begin a session of the C2S protocol (Proper aspect) the place they use the “ephemeral” keypair (z, Z) and the corresponding vouch field EK2 (Z) (in blue) so as to authenticate as U to the server.
Enlarge / A determine exhibiting the cross-protocol interplay of an E2E and a C2S session. The attacker claims the general public key of the server and is aware of a keypair of the shape (z, Z = 0x01 ∥ σ ∥ 0x01). They persuade the sufferer U to ship σ to them as an E2E textual content message (in blue, Left aspect). The attacker can now begin a session of the C2S protocol (Proper aspect) the place they use the “ephemeral” keypair (z, Z) and the corresponding vouch field EK2 (Z) (in blue) so as to authenticate as U to the server.
- When an attacker has compromised a Threema server:
- A scarcity of integrity safety on the message metadata. In consequence, an attacker can surreptitiously reorder and/or delete messages despatched from one shopper to a different.
- Defective utilization nonce dealing with permits for “replay and reflection” assaults, through which the menace actor resends previous messages and sends a consumer a message that consumer beforehand despatched to another person.
- A bug within the challenge-and-response protocol used for a shopper to authenticate itself to the server throughout registration. Throughout the course of, the shopper proves possession of its non-public key by encrypting a server-chosen message that’s encrypted with a server-chosen public key. A compromised server can exploit this design to create “kompromat,” or doubtlessly incriminating messages that may be delivered at any later time to a focused consumer. Threema patched this vulnerability in December 2021, when a separate researcher noticed it.
- When an attacker features entry to an unlocked cellphone operating Threema:
- A characteristic that enables customers to export their non-public key from one system to a different. Poor design selections make it trivial for an attacker to make use of the important thing to clone a Threema account and go on to entry all future messages. Mixed with a compromised Threema server, the adversary can even acquire all beforehand despatched messages.
- Message compression that happens earlier than encryption when Threema creates a backup, mixed with the power for an attacker to make use of a nickname characteristic to inject chosen strings into the backup. This enables a extra refined attacker to watch the scale of the backup file over a number of iterations and ultimately get better the consumer’s non-public key.
[ad_2]
Source link








