[ad_1]
Federal Reserve officers warned they would wish to see “considerably extra proof” of easing inflation earlier than they’re satisfied that value pressures are beneath management as they backed recent charge rises this 12 months, in line with an account of their most up-to-date assembly.
Minutes from the December gathering, when the US central financial institution raised its benchmark charge by half a proportion level, confirmed the Fed intends to proceed squeezing the financial system to attempt to sort out value pressures, which they warned may “show to be extra persistent than anticipated”.
The half-point rise ended a months-long string of 0.75 proportion level will increase and lifted the goal vary of the federal funds charge to between 4.25 per cent and 4.5 per cent.
The choice in December adopted recent proof that inflation appeared to have peaked as power costs and people tied to the products sector have retreated, developments which individuals described as “welcome”.
“Members usually noticed {that a} restrictive coverage stance would have to be maintained till the incoming knowledge supplied confidence that inflation was on a sustained downward path to 2 per cent, which was more likely to take a while,” the minutes, launched on Wednesday, mentioned, referring to the Fed’s inflation goal.
The minutes additionally indicated that officers are attuned to how their coverage communications are being digested by buyers and others throughout Wall Avenue. Within the weeks main as much as the December assembly, monetary situations had loosened as merchants in fed funds futures wagered the Fed would again off its tightening marketing campaign earlier than officers have signalled.
A slower tempo of charge rises “was not a sign of any weakening of the committee’s resolve to attain its price-stability aim or a judgment that inflation was already on a persistent downward path”, quite a few individuals mentioned, in line with the minutes.
Officers additionally warned an “unwarranted easing in monetary situations, particularly if pushed by a misperception by the general public of the committee’s response operate, would complicate the committee’s effort to revive value stability”.
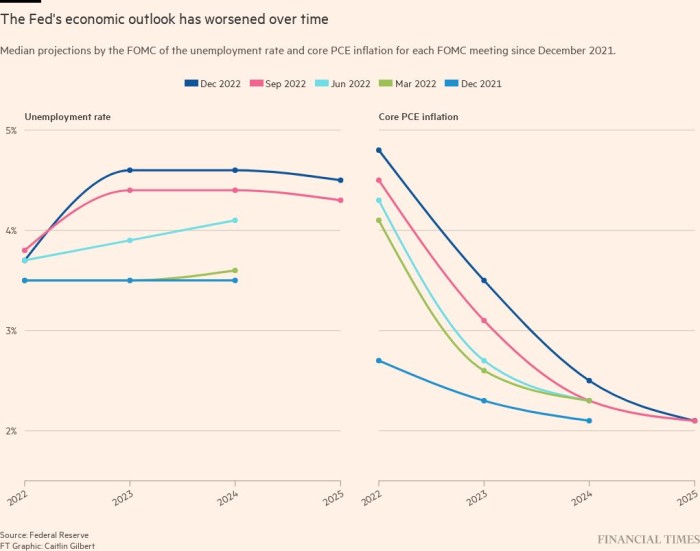
In keeping with the “dot plot” of policymakers’ interest rate projections printed after the assembly, most officers now see the federal funds charge peaking between 5 per cent and 5.25 per cent, with a big cohort of the view that it might have to go even increased. That means a complete of a minimum of 0.75 proportion factors’ value of charge rises to come back.
On the press convention that adopted final month’s charge resolution, Jay Powell, Fed chair, warned that he couldn’t “confidently” say the central financial institution wouldn’t elevate its estimates once more as he sought to push back towards hypothesis that it will quickly abandon its tightening plans.
“We’ve coated a number of floor and the complete results of our fast tightening up to now are but to be felt. We’ve extra work to do,” he advised reporters.
The dot plot confirmed that charge cuts usually are not anticipated till 2024, when the benchmark charge is projected to fall to 4.1 per cent, earlier than dropping to three.1 per cent in 2025. Progress is ready to sluggish significantly as borrowing prices are stored excessive for an prolonged interval, with most officers projecting an growth of simply 0.5 per cent this 12 months earlier than a 1.6 per cent rebound in 2024.
The unemployment charge is more likely to improve by practically a full proportion level from its present degree to 4.6 per cent, the estimates present.
Whereas the weakening financial system is ready to place downward strain on costs, it’s anticipated to take a while for inflation to fall to the Fed’s longstanding 2 per cent goal. The central financial institution’s most well-liked inflation gauge — the core private consumption expenditures value index — is projected to say no to three.5 per cent by the tip of 2023 and a pair of.5 per cent in 2024. As of November, it hovered at 4.7 per cent.
To date, the Fed’s tightening has been felt most in interest-rate delicate sectors akin to housing, the place costs have declined dramatically from their coronavirus pandemic peaks. Nonetheless, labour demand stays excessive as customers proceed to spend, serving to to additional entrench inflationary pressures which have taken maintain throughout the services sector. Economists warn that rooting these out would require a recession and job losses.
Powell and his colleagues, in addition to White House officials, keep a recession might be prevented even because the unemployment charge ticks up.
[ad_2]
Source link