[ad_1]
Key information indicators counsel that this 12 months’s rampant global inflation has peaked and that the tempo of headline worth development is ready to gradual within the coming months.
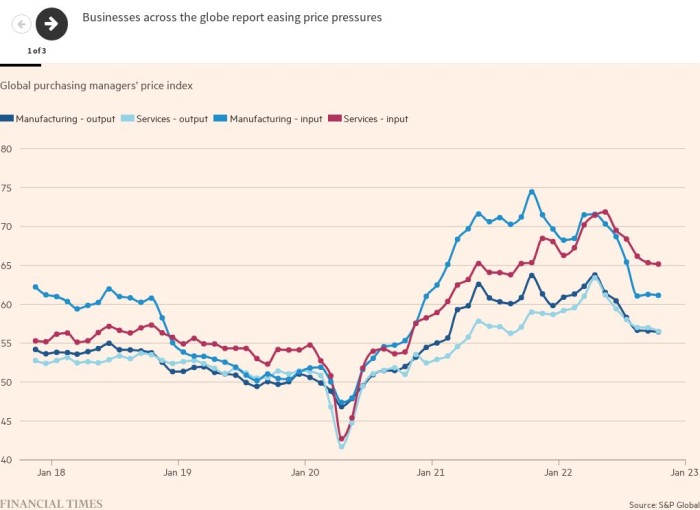
Manufacturing unit gate costs, transport charges, commodity costs and inflation expectations have all begun to subside from their current file ranges. These information sequence are extensively watched by economists and policymakers as they supply an early indication of the tendencies that may form the headline inflation calculation.
In line with economists, the figures counsel that worth pressures on international provide chains are easing, making it doubtless that headline inflation will fall from the traditionally excessive charges that hit family funds and enterprise exercise in current months.
That might be welcome information for leading central banks, which have been elevating interest rates quickly in a co-ordinated effort to tame inflation, risking plunging main economies into recession by doing so.
“Inflation is probably going at its apex,” mentioned Mark Zandi, chief economist at Moody’s Analytics. The easing of worth pressures and provide supply bottlenecks “presage the approaching moderation in shopper costs”, he mentioned.
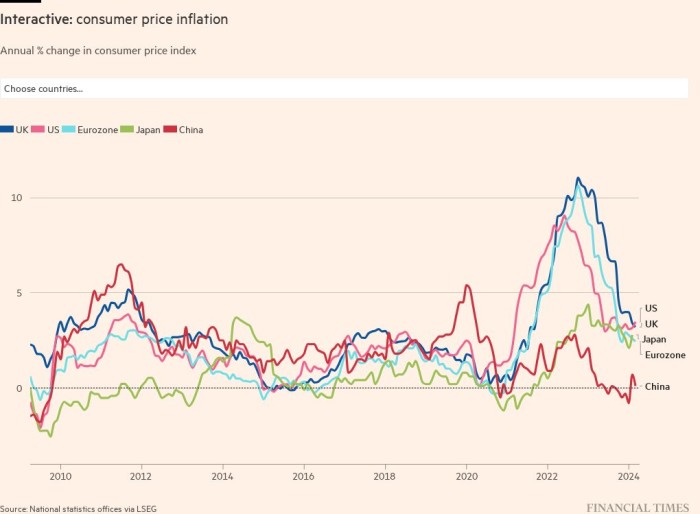
International inflation hit a record 12.1 per cent in October in keeping with Moody’s estimates; that would be the “excessive water mark” for shopper costs, Zandi mentioned.
Inflation has already peaked throughout rising markets, in keeping with Capital Economics, with shopper costs falling in Brazil, Thailand and Chile, whereas current information reveals a weakening of some worth pressures in developed economies.
In Germany, manufacturing facility gate costs fell 4.2 per cent in October in contrast with the earlier month — the most important month-to-month fall since 1948. In the US and the UK, annual producer worth inflation has been slowing for the reason that summer season.
Almost all of the G20 group of main economies which have launched their October producer worth indices reported a slower tempo of annual development than within the earlier month, together with Spain, Mexico, Portugal and Poland.
Jennifer McKeown, chief international economist at Capital Economics, expects international headline inflation to start to fall subsequent 12 months on the again of decrease costs for many commodities as demand weakens. Excessive vitality costs this 12 months would flatten out in 2023, she mentioned.
“Our estimate is that meals and vitality results collectively will knock about 3 share factors off headline shopper worth inflation within the superior economies on common over the following six months,” she mentioned.
Nevertheless some economists cautioned that continued excessive vitality prices might gradual the decline. Susannah Streeter, senior funding and markets analyst at Hargreaves Lansdown, mentioned that “oil [is] set to remain extremely delicate to produce constraints, and the looming EU ban on Russian crude” would proceed to gasoline headline inflation within the UK and the eurozone.
Costs for vitality and different commodities might leap once more if the Chinese language economic system makes a powerful restoration, or if Russia makes additional export cuts in retaliation for western worth caps on its oil and fuel.
Commodity costs and different indicators which feed into the general headline inflation determine are falling.
The FAO food price index slowed to an annual rise of 1.9 per cent in October, method down from a peak of 40 per cent in Could 2021. The TTF benchmark European fuel worth is beneath €130 per MWh, down from a peak of €311 in August and most commodity costs are nicely beneath their peaks.
International transport charges have returned largely to pre-pandemic ranges after rising by greater than 5 occasions in the course of the lockdowns.
Within the US, manufacturing and providers prices rose on the slowest tempo since December 2020 in November, whereas promoting worth development fell to its slowest fee in over two years, in keeping with the S&P International buying managers month-to-month survey. Within the eurozone, inflation in manufacturing facility gross sales reached a 20-month low, the survey discovered.
Buyers’ expectations of the place inflation shall be 5 years from now have stopped rising, reflecting the current aggressive financial coverage tightening by many central banks.
US inflation fell by greater than anticipated in October and most economists forecast the tempo of worth development will peak this quarter within the UK, the eurozone and Australia. Economists polled by Reuters count on eurozone inflation to hit 10.4 per cent in November when the info is revealed in Wednesday, a decline from 10.6 per cent for the earlier month.
Nevertheless, whereas it’s more likely to fall from its peak, international inflation is ready to stay above central banks’ long-term targets, economists mentioned.
“Don’t count on inflation to drop all the way down to 2 per cent [the target rate in most advanced economies] in a short time,” mentioned Katharine Neiss, chief European economist for PGIM Mounted Revenue.
Core inflation, which excludes vitality and meals, is predicted to peak later for a lot of nations, because the influence of excessive vitality costs on the broader provide chain shall be “drawn out”, she warned.
Nathan Sheets, international head of worldwide economics at Citi, mentioned that whereas many indicators level to “a pointy decline in inflation for a lot of kinds of items”, excessive inflation “is probably going for a while to come back [and] a lot of the approaching 12 months at the least”.
[ad_2]
Source link